Business Analytics is not a new kid on the block. The idea may appear very modern, yet the roots of BA are from the 1800s. Ledgers, which were used for initial accounting and inventory management, inscribed the first steps towards data-led decisions, leading to the evolution of business analytics. More importantly than these rudimentary records, some more structured approaches to management were born in the early 1900s, due mostly to the industrial revolution and the growth of manufacturing.
More Structured Approaches to Management — By the early 1900s, with the industry and manufacturing taking a big turn towards order-based operations, there was a need for more structured approaches to management. The first real application came in the form of the establishment of an analytical, systematic approach to optimize operations for greater efficiency.
However, by the 1950s, with computers being developed, businesses started to experiment in data processing techniques. The early mainframe computers, while hardly high-powered enough to do it all automatically, were faster in their processing and storage of data than anything a man could do. These advances marked the beginnings of rudimentary corporate or management information systems.
Till the 1980s, several corporations started using computers for less but widespread businesses. Within these years, companies began fielding star DSSs — the earliest decision support systems. The systems comprised data and analytical models to help business make decisions.
1980–2000: Era of Databases, Spreadsheets and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems In the intervening years, most companies started introducing relational database management systems, began somewhat rudimentary data mining and reporting by using relational databases. Business Intelligence (BI) became a field with structured tools and technologies for data access and analysis.
Analytics embarked on a different level in the early 21st century (2000–2010). Big Data, cloud computing, and the internet were the new parity to revolutionize the way businesses gathered and made sense of the information. As a result, data warehouses, online analytical processing (OLAP), and advanced dashboards grew increasingly more popular.
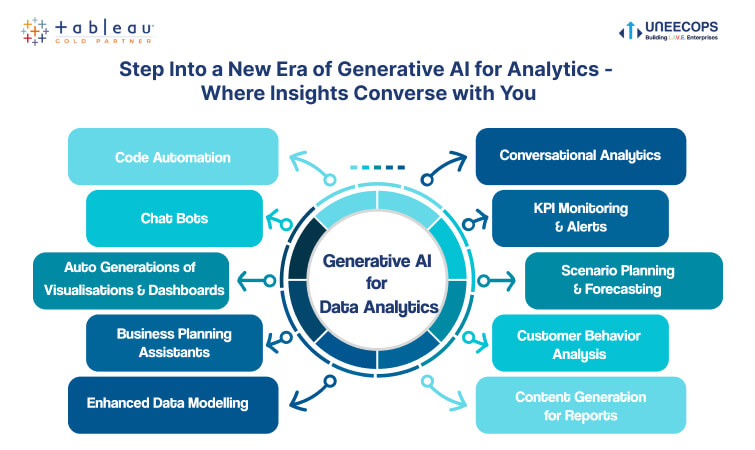
Now, in the 2020s, we are actually seeing the full flowering of business analytics. Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and real-time analytics are changing the decision making by influencing how and what decisions are made. Everything from social media, IoT devices and customer feedback tools is now mined by businesses for structured and unstructured data. The history of data analytics and the evolution of business analytics have become fundamental to the decision-making processes as we know them today.
BI Lingo Explained: Making Sense of Analytics Types
A modern twist on Business Analytics, which comes with an array of terminologies and analytic types that reveal the extent and nature of the analysis:
- Descriptive Analytics is the root level and talks about what has happened in a business. It consists of pattern and trend identification tools like dashboards & reports, with the help of historical data.
- Diagnostic Analytics: Going beyond “what happened,” delves into “why it happened” by pinpointing root causes. Drill-down, data discovery, and correlations are some of the common techniques.
- Predictive Analytics: Gives an answer to the question “What is probable of occurring?” This answers what is most likely to happen using statistical models and machine learning algorithms. Know More About Predictive Analytics….
- Prescriptive Analytics: The one you have to decide for yourself and answer the question, “What should we do?” It prescribes actions by scenario engine evaluations of prospective scenarios with AI and simulation models.
- Cognitive Analytics: Another human reasoning style of AI, that can consume unstructured data, make decisions, and sometimes learn over time.
Together, these types of analytics form the foundation of Business Intelligence (BI) that drives further insights and enables businesses to make wise decisions.
Analytics Trends You’ll Be Talking About in Every Boardroom
Evolution of Business Analytics has shown a lot of change for the better into the future. The notable trends for the forecast include:
- Hyperautomation: Using AI, ML, Robotic Process Automation (RPA), and other capabilities in one ecosystem (software) to automate everything.
- Augmented Analytics: Utilizing AI and ML to perform data preparation, insight creation & explanation at scale, thus presenting as a testament to the evolution of analytic scalability.
- Data Democratization: You will get better tools for deep data-science and make as many employees as possible able to generate insights as possible.
- Real-Time Analytics: The need for moment-based views will drive real-time data processing and decision-making.
- AI & Analytics Governance: With the power of analytics increasing, we will see an increased focus on ethical utilization and data governance around things like privacy and bias in algorithms.
- IoT and Edge Analytics Integration: Analytics will move towards closer proximity to the source of data and place the smart devices, with faster and localized decisions.
The high speed at which these innovations are occurring creates an urgency for businesses and professionals to remain updated and flexible.

Struggling with Business analytics reports?
Why Business Analytics Is No Longer a Luxury
Business Analytics is a business strategy, not a luxury anymore. The evolution of business analytics has made it more approachable, thus increasing availability and necessity at the same time.
- Data-Driven Choices: Business Analytics makes data streamlined for companies and removes the dependence on experience.
- Cost Reduction: Analytics in a systematic approach for resource optimization and operation optimization can ensure cost savings by a large margin.
- Insights of the Customer: Analytics gives businesses information about the customers themselves, what they do, and how you can improve customer satisfaction.
- Competitive Advantage: Analytics enables companies to identify trends more quickly, innovate faster, and outperform competitors.
- Risk Management: Predictive analytics enables a prediction regarding risks and therefore empowers organizations to implement mitigation strategies.
- Operational Efficiency: In-built real-time dashboards and performance monitoring give room for process optimization to get things done faster.
Industries including finance, healthcare, retail, education, and logistics are all employing transformation of Business Analytics to drive industry-specific operations and a competitive advantage. As data continues to pile up — in larger amounts, of different varieties and volume— business analytics will become even more critical for survival and success.
Conclusion
Business Analytics goes a long way from old pen and paper ledgers in the 1800s to real-time, AI-driven views today—it reminds you of an interesting interplay of thoughts, technologies, and strategies. Now it is a must for how companies do, grow, operate, and innovate.
In the near future, as the evolution of business analytics continues, it will become bigger in scope, impacting everything from daily operations to long-term strategic planning. The more analytics companies can bring to play, the better their ability to deal with intricacies in the digital world, hence leading to smarter and faster decisions.